
By Rahnuma Ahmed
?
?Only when the last tree has withered, and the last fish caught, and the last river been poisoned, will we realise we cannot eat money.’
Cree proverb
?[the] uprootedness and superfluousness which have been the curse of modern masses since the beginning of the industrial revolution and have become acute with the rise of imperialism at the end of the last century and the break-down of political institutions and social traditions in our own time.’
Hannah Arendt, The Origins of Totalitarianism, 1975
?You cannot eat coal’
?No, we do not want the coalmine. What will we eat?’ said an elderly woman. I was watching raw, uncut video footage from Phulbari, shot by media activists Zaeed Aziz and Farzana Boby, a couple of days after the killings occurred on August 26, 2006.
Another woman steps into the frame. She vents bitterly, we work daily for our subsistence, we eat from what we earn. That is all we have. If this land is turned into a coalmine, those who eat in exchange of daily wages, where will they go? Where will we live? How will we survive?
Zaeed and Farzana’s film, ?The Blood-Soaked Banner of Phulbari‘, was released soon after the killings in 2006. I watch the beginning sequence. A crowd of men stand at the long-distance bus stand in Phulbari town, they talk to each other and to the film crew. ?We are poor people,’ says a man, probably in his late-thirties. ?If I lose my home, how will I earn a living? What use will be the coalmine?’ Who will it benefit?
I return to clips from their uncut footage. A younger woman is sitting in her courtyard, ?No, I don’t have a husband, I live with my mother, I work with her. In the same place. If the coalmine comes, we, that is, us mothers-and-daughters, where will we go? We will be scattered from our relatives, we will lose our ties.’
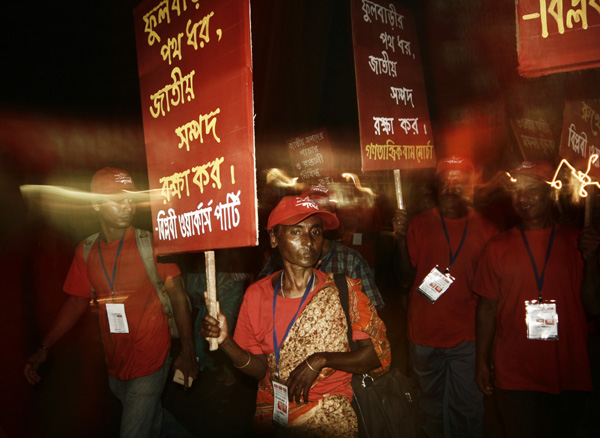
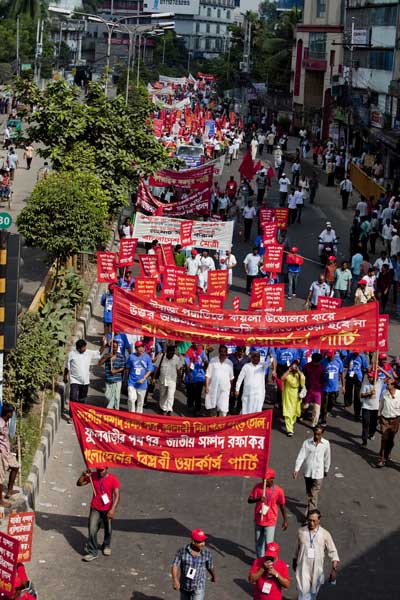
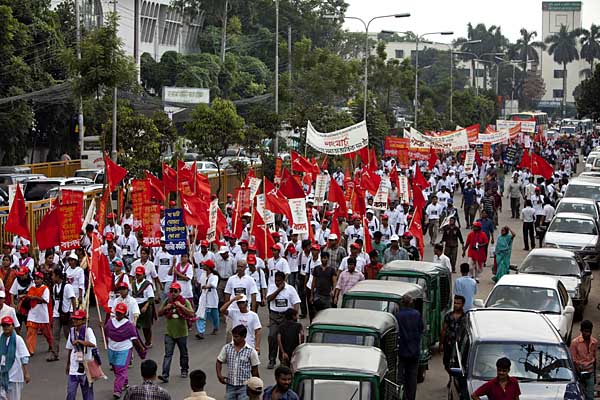
 The August 2006 protests in Phulbari ? Andrew Biraj/Drik/Majority World
The August 2006 protests in Phulbari ? Andrew Biraj/Drik/Majority World
?Where will we go?’ This question is repeatedly raised by villagers, by both men and women, old and young, by farmers, day-labourers, petty businessmen, schoolchildren, college-going youths, both Bengalis and adivasis, who belong to Santal, Oraon, Pahan, Mahali and Munda communities. By Hindus and Muslims.
?Two coalmines have been built in neighbouring areas,’ one of the men standing at the bus-stand in the Blood-Soaked Banner documentary had said. ?What development has it brought, tell me?’
I turn to Ronald Halder and Philip Gain’s film, ?Phulbari’, an activist film released by SEHD earlier this year. Abdul Jalil of village Chouhati turns his face away in pent-up anger when asked how he has benefited from the coalmine in Barapukuria. ?Benefit? How have I benefited? It has crippled me. I cannot describe the damage it has done. Those who have benefited from it have. We have been devastated.’
Azizunessa of the same village does not mince her words. She too has suffered from the Barapukuria coalmine. ?We are poor people, we raise a cow, a goat or two. But the security guards, they do not let us enter, they do not allow us to cut even a blade of grass. So how does the coalmine that they have built, help us? How do I get my bowl of rice? They do not give me work in the coalmines. My sons have no food. How will they live? Only Allah knows what our situation is like. How our days pass. Or don’t. I did agricultural work, I winnowed paddy, I worked, I ate, I brought in one and a half seers of rice from the house I worked in, I fed the children. Work is not something that appears out of nowhere, that daughters-in-law can bring, that poor people can give each other. Why is it that the coalmine has stopped me from working, from feeding myself? The coalmine is protected by barbed wire fences, it is surrounded by high walls. Why?’ Who benefits from the coalmine?
The Phulbari coal project plans to extract coal using open-pit mining method in seven unions and one municipality in four upazilas of Phulbari, Birampur, Nawabganj and Parbatipur in Dinajpur district. The company behind the $1.4-billion project is Asia Energy Corporation (Bangladesh), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the British-registered Global Coal Management Resources Pls. According to Asia Energy, 40,000 people would be involuntarily resettled, 10,000 hectares, primarily of fertile agricultural land, would be required for mine and associated infrastructure. Activists say the number of people evicted is likely to be ten times more. The proposed coal project would divert a river, suck an aquifer dry for thirty years, the life span of the project. Dynamite explosion, environmentalists say, would cause noise and dust pollution, this would be increased by the trucks and trains that will haul away the coal to the port in Sundarban. To prevent flooding, huge pumps will pump out 800 million litres of water daily, from the mine. This will lower the groundwater in an area covering 500 square kilometres. Air and water pollution is likely to spread to surrounding water bodies. Asia Energy plans to create a huge lake after the project is over, but activists predict that the water is likely to be toxic.
GCM has a sustainable development manager who guides their approach. But the global record of mining operations rejects the sustainable development myth. Roger Moody, international researcher and campaigner against exploitation caused by multinational mining, writes in ?Rocks and Hard Places: The Globalization of Mining’, lesser-developed countries, those with a high degree of dependence on mining, show slower rates of economic growth than their peers. Some countries, he writes, have been worse off. Potosi, a region that has been mined for silver for five centuries, is one of the poorest in Bolivia. Closer home is Orissa, Bihar and Jharkand which provide most of India’s minerals. Bihar has been for many years India’s ?least developed’ state, while Orissa, in 2005, was ranked as the ?poorest’ in the country. Mined regions even in advanced and middle-income countries have been the last to share in aggregated wealth. In 1870, Cornwall had 2,000 tin and copper mines. When the last pit was closed in 1998, Cornwall had the highest proportion of low-paid workers. Mineral-dependent economies, largely in Africa, are more likely to experience zero or even negative growth, since labour and capital move away from sustainable sectors to the extractive sector, and domestic products lose their competitive edge on international markets.
And of course, ?understanding’ risks, albeit from a safe distance, is not the same as being willing to undergo it oneself. Recently, activists from the Alberta Environmental Network showed up at the Oil and Gas Investment Symposium in Calgary, Canada, held by the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers. The event brought together 85 companies and 375 investors from Canada, the US, and around the world. Those present at the meeting were offered drinking water that Athabasca Chipewyan First Nation peoples claim is toxic. They experience high rates of rare cancers and auto-immune diseases, which they believe are linked to the development of the tar sands.
None of the producers/owners, investors, CEOs drank the water.
26th August 2006
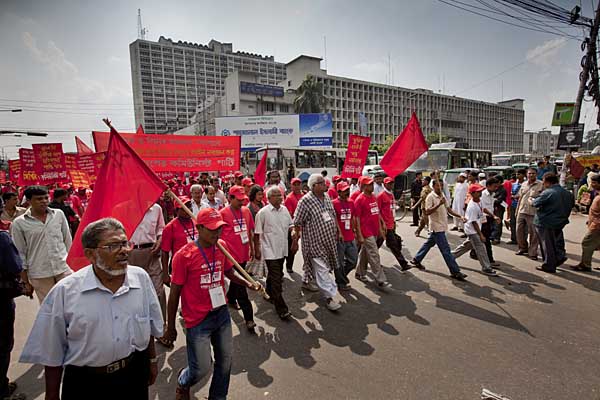
On August 26, 2006, more than 50,000 people took part in protests against the proposed mine, in Phulbari town. People from adjoining towns and villages poured in. The Bangladesh Rifles, a paramilitary force, opened fire on the protesters. Three young men, Tariqul, son of the municipal commissioner and panel chairman, Ameen, a young carpenter, and Salehin of the adjoining upazila Nawabganj died instantly. One to two hundred people are reported to have been injured in the violence unleashed by the BDR and police.
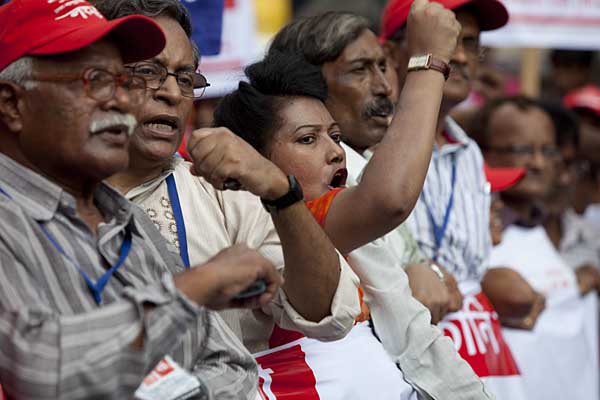
I turn to Zaeed and Boby’s uncut video footage. A woman describes angrily, ?It was around maghreb, just before the call for prayers, the photographers had left, TV reporters too, that’s when they attacked us.’ To leave no photographic evidence? Another woman butts in, ?We had chased out the police, I was so furious, I have never had the courage before, since that day I have learnt how to fight. Now, I have limitless courage. I am not afraid to die.’ The woman speaking earlier returns to her story, ?The military [read BDR] began beating up people, they entered into our homes, they tore down the tin roofs.’ She is indignant, ?These are people who are meant to protect us, they are law-enforcers.’ Another woman speaks up, ?Did any of them die? They never do. Did any of them suffer any injuries?’
A woman who was badly beaten says, ?The BDR entered our villages, they went from house to house. How dare they enter our villages? So we chased them out. But then they regrouped, they came after us. I couldn’t escape, they caught me and beat me very badly.’ The shot shows other women in the courtyard, nodding their heads as they listen.
Off-screen I hear a female voice, ?Can the government ever defeat the janata?’ A woman wearing a printed sari on-screen says, ?It is the government which breeds terrorists, they tear down the shops of poor people, they snatch away cigarettes and other items, they break these little cigarette stalls that are run by young boys for a living.’ Another off-screen voice, also a woman’s, speaks up, ?Ordinary people are never terrorists.’
Most of the women, in no uncertain words, condemned Khaleda Zia, the then prime minister, for having sold out the interests of the country. What kind of a woman is she? Sending soldiers after us, dragging our husbands out of our homes. Does she want to make us widows? Their language was laced with four-letter words, often directed at her, at times at the then energy ministry adviser, Mahmudur Rahman, sometimes at the whole cabinet. I brought up the issue with Nurul Kabir, the editor of this paper. He said with a wry smile, ?I am most respectful of subaltern languages, but wouldn’t it offend bhodrolok sensibilities?’ We laugh and talk about the gentrification of language, a class-ed mechanism of ruling. Who was it who had said there can be feelings without language, but no language without feelings? Was it not the historian Collingwood? I muse over issues of language, of home and belonging as I search the web and read through newspaper reports of the 26th, and after. I come across news reports stating the energy ministry adviser, Mahmudur Rahman, blamed a ?small group of leftist parties without any influence whatsoever’ for orchestrating the deaths and injury to people at Phulbari. Asia Energy Bangladesh’s CEO Gary Lye’s words mirror Mahmudur Rahman’s, ?It’s up to the government, but it would appear to us that the unforgivable events and the needless loss of life and suffering that took place in Phulbari are entirely the fault of the organisers.’
Those who campaign against the ruthless exploitative practices of trans-national mining companies say, increased investment results in human rights abuses, especially against rural communities which the companies want to dislocate and uproot. They also say that the role of the state in extractive sector governance and citizens’ protection diminishes, while its role in protecting and promoting the interests of trans-national corporations increases. One sees that happening in Phulbari, over Asia Energy’s proposed Phulbari coal project.
Mozammel member, a pourasabha member, says in defence of the project, ?If the government wishes it, how can we prevent it from happening?’ People around him ask, ?But why do you want the coalmine? Can you not see that it is not in the interests of the people?’ His answer is cruel and simple, ?We are not for the people. We are for the government.’
The compensation story
In the Blood-Soaked Banner, a man who describes himself as a petty businessman says, ?Yes, the coal project will bring benefits to some, to those who have built three-storey buildings in the town, those who have made plans of where to relocate, where to build new homes, the businesses that they will start, even, what kind of houses they will build for themselves.’ It will benefit those already-privileged, those who are townspeople. But not those who live off the land, those who make a living from agriculture, from day-labour, and the innumerable number of ways through which poor people make a living. In other words, the majority.
Abdul Jalil of Chouhati, Barapukuria was asked about the compensation that he had received from the government. ?They gave it in little, little instalments, it took ages, the money dried up as I walked back and forth to collect it.’ Compensation is also tied up with land deeds and titles, a method of possession and ownership that is antagonistic to the adivasi tradition, and their claims to ancestral land. That is probably why Lawrence Tudu of Buski, Birampur says, ?We will not leave this village, we will not leave our homestead, we will not leave the soil, if necessary, my remains will get buried under this soil.’
Poor people’s claims to compensation are entangled in bureaucracy, and in corporate controlled channels of profiteering. Corporations themselves evade responsibility and accountability as one sees in Magurcchara and Tengratila, where international oil companies have shown great reluctance to pay compensation for the miserable accidents that have occurred.
And compensation for killings? Ameen’s mother when asked said yes, I have received two lakh taka from the government, as compensation. And another twenty thousand from Sheikh Hasina, leader of the Awami League, the then opposition party (interestingly enough, it was the Awami League government that awarded the licensing agreement to Asia Energy, in 1998). But, she says, I hurt, I grieve for my son. I raised him, does compensation lessen my loss? Will money ever call out ?ma’, or ?baba’?
Democracy, a world of power
Democracy, writes historian and subaltern theorist Partha Chatterjee in his recent work, ?The Politics of the Governed’, is no longer government of the people, by the people, and for the people. Twentieth-century techniques of governing population groups, widespread acceptance of the idea of popular sovereignty, the creation of governmental bodies that administer populations but do not provide its citizens with arenas of democratic deliberation, these conditions, says Chatterjee, give rise to democracy becoming a world of power. A world which has startling dimensions, and unwritten rules of engagement.
I see the people of Phulbari voice a collective identity, framed, at first, within the politics of electoral democracy. We have brought this government to power. How can they not do what we want? It is my vote that decides who will be the member of parliament. I elect the chairman. He must work for me, in my interests. A woman adds, what kind of a government is it that pushes us into waging movements? That destroys our peaceful lives, that takes away our sons? We want to return to our normal lives. Increasingly, people’s voices become more assertive. If the government does not value us, we will not value them either. If the government will not provide for us, we do not need this government. We do not need any government.
Amidst the strident assertiveness, a peasant’s words ring out clearly, ?I am a khetmojur, I till the land. It is the crops I grow that feed the leaders. Am I more valuable, or they?’
Whether elected or un-elected, all governments, both leaders and state functionaries, need to be fed. They would be well-advised to listen to the voices of those who produce. After all, one cannot eat coal. Or money, either.
First published in New Age on 19th August 2008?
Other articles that refer to Phulbari:
Profits versus the Poor
A Beginner’s Guide to Democracy
Bangladesh Now
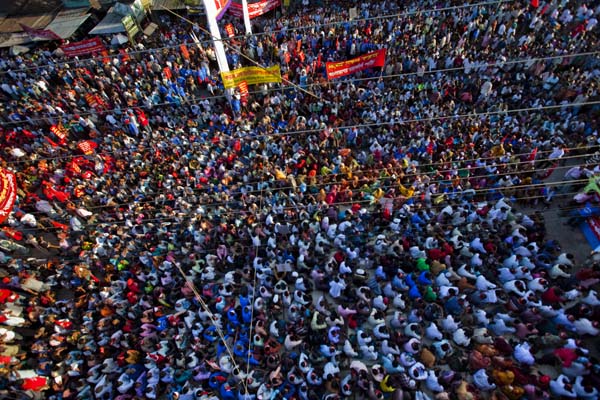
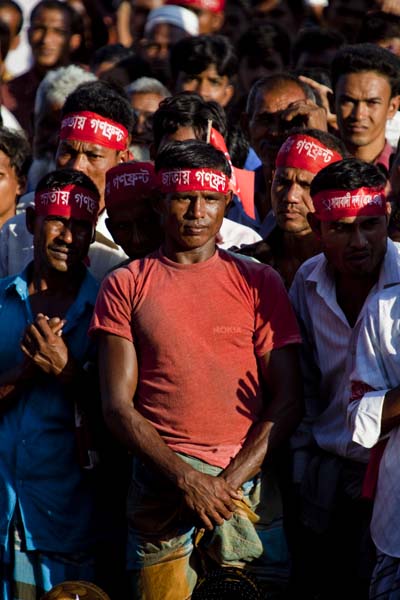
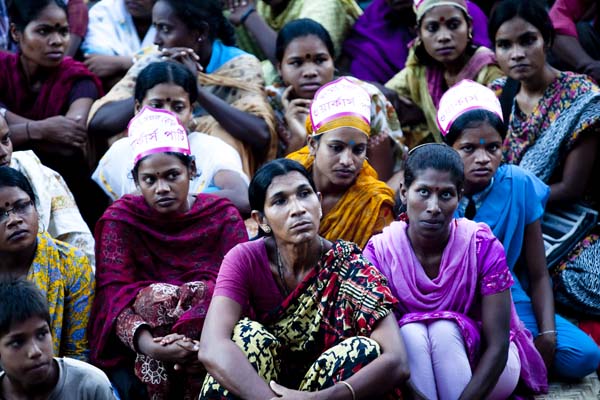
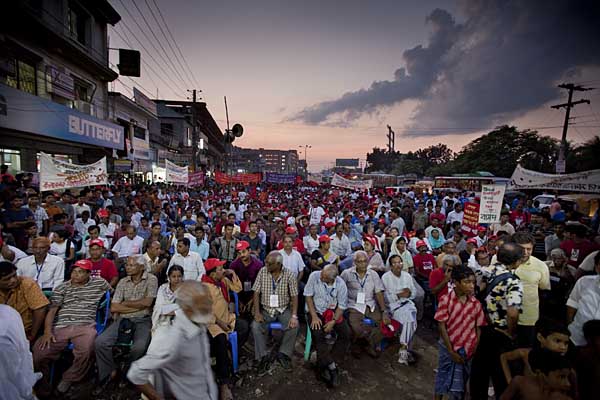














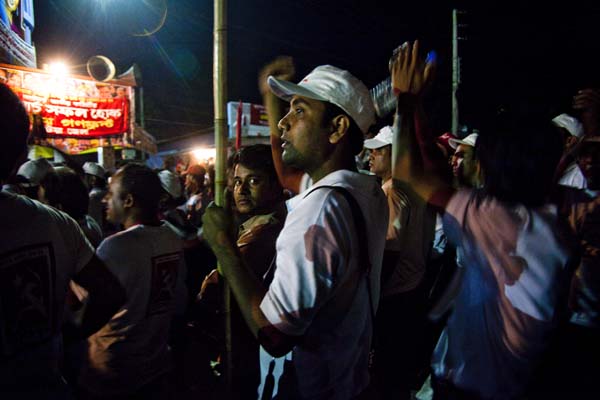















 ?I have lost a son, maybe I?ll lose another, but I won?t let them setup a coalmine here.? To Tahmina Begum who had lost her son Toriqul to police bullets, her land was also her family.
?I have lost a son, maybe I?ll lose another, but I won?t let them setup a coalmine here.? To Tahmina Begum who had lost her son Toriqul to police bullets, her land was also her family.  It could have been a ?B? rated western except that it is set in the east.
It could have been a ?B? rated western except that it is set in the east.  People wanting to hang on to their ancestral land versus mining companies wanting huge profits. There have been only minor changes from previous scripts. When farmers wanted fertilizers and seeds, the police had opened fire killing them, when they wanted electricity to irrigate their soil, the police had opened
People wanting to hang on to their ancestral land versus mining companies wanting huge profits. There have been only minor changes from previous scripts. When farmers wanted fertilizers and seeds, the police had opened fire killing them, when they wanted electricity to irrigate their soil, the police had opened  fire killing them. Now that they want to retain their land rather than have it converted into coal mines again the police have opened fire killing them.
fire killing them. Now that they want to retain their land rather than have it converted into coal mines again the police have opened fire killing them.  The Shaotals, being indigenous minority groups, find themselves even more vulnerable within this persecuted community. In the shootings on the 26th September 2006, in Phulbari, Dinajpur, in northwestern Bangladesh, at least six villagers are known to have been killed, over a hundred are said to be missing.
The Shaotals, being indigenous minority groups, find themselves even more vulnerable within this persecuted community. In the shootings on the 26th September 2006, in Phulbari, Dinajpur, in northwestern Bangladesh, at least six villagers are known to have been killed, over a hundred are said to be missing.